
Sunflower losses are a symptom of chemistry, not “just white rot”
Greening agro is not a fad, but a reaction to the fact that excess nutrients are becoming a source of soil and water pollution, and biodiversity loss.
In the world of modern medicine, we are on the verge of a real revolution. If a decade ago, genetic editing and cell cultivation seemed like fantasy, today they are becoming a reality — not only in laboratories, but also in clinics. Gene therapy and cell therapy are two interconnected areas that are opening a new era of treatment for diseases that were previously considered incurable.
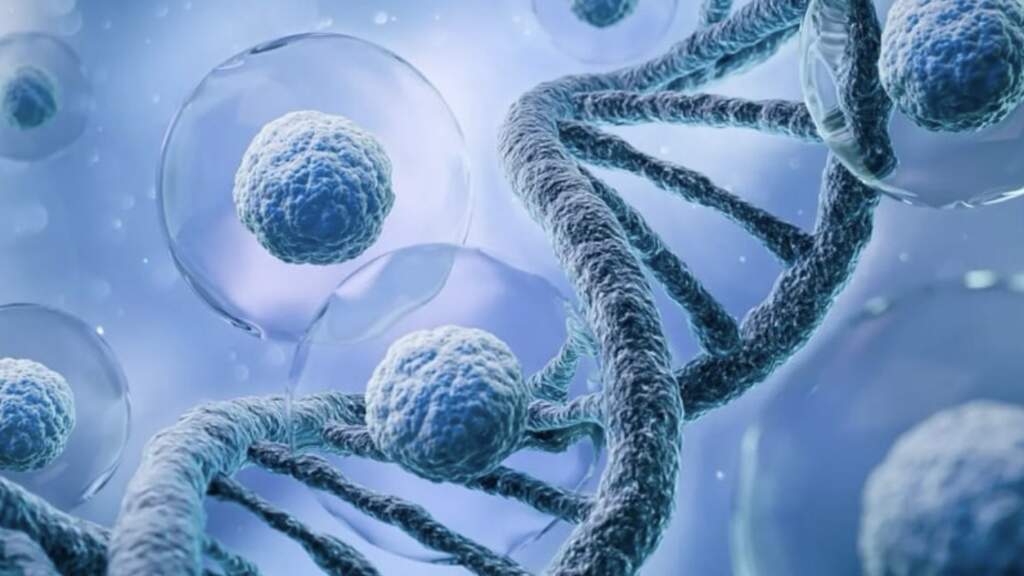
Gene therapy is a treatment method in which genetic material is introduced or altered into human cells to correct or replace defective genes.
Simply put, instead of fighting symptoms, doctors work with the cause — at the DNA level.
Modern technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9 allow us to “edit” genes with high precision, correcting mutations that cause hereditary diseases: muscular dystrophy, hemophilia, sickle cell anemia, etc.
Cell therapy is a method in which living cells are injected into the body to repair or replace damaged tissue. This can be:

Today, science is moving towards combining gene therapy, cell therapy, and artificial intelligence.
AI helps predict which changes to the genome will have the best effect, and 3D bioprinting allows you to create tissues and even organs from a patient’s cells.
Thanks to international research and the participation of Ukrainian scientists, these technologies are gradually moving from experiments to clinical practice.

Greening agro is not a fad, but a reaction to the fact that excess nutrients are becoming a source of soil and water pollution, and biodiversity loss.

Digestate with biochar and glauconite is an innovative organo-mineral composite for reducing nutrient losses, prolonged plant nutrition, and increasing soil fertility.

Soil degradation and water pollution are increasingly merging into a combined environmental crisis, especially in arid and post-industrial regions.